Creating server backups allows you to ensure data safety and protection against data loss, if the system fails. Lack of regular backup creation can put you at risk of losing files and data (the operation of the entire system may also be disrupted). You can copy:
- virtual machines (VM);
- separate files;
- disks or disk partitions;
- a group of files combined according to some characteristic;
- operating system.
In order to quickly restore data in case of any errors or failures, it is necessary to regularly create backups. servers or devices located in different spaces are the best option for storing backups.
Another reliable and convenient way to store data is using S3 Object Storage. This option makes it possible to access backups from anywhere in the world. Cloud storage provides a guarantee of data security, as it has a high level of protection. If necessary, the capacity of such storage can be increased. If you need to rent S3 Object Storage, we recommend our partners – 3HCloud. They provide a large number of services aimed at achieving any of your business purposes using computing resources and data storage functions.
Why are backups required for databases and websites?
In the event of system failures, administration errors or virus attacks, information may be damaged or completely lost. To prevent this from happening, backup copies are used. After server failures or hacker attacks, website operation can be quickly restored thanks to backups. The safety of important information stored in the database is ensured by database backups (including information about payments, customers, orders, etc.). Backups give an opportunity to quickly restore data and continue normal system operation.
Let's consider the reasons why it is important to make backups:
- Burglary protection. Backups makes it possible to quickly restore the operation of a database or website in case of a hack or virus attack.
- Loss protection. Reasons for loosing data may be different: virus attacks, system failures or any natural disaster. Backups provides an ability to save copies of important data and quickly restore them.
- Avoiding downtime. Backups also help to reduce the risk of losing income and customers as well as the likelihood of problems occurring in the operation of the site or database.
- Testing new updates and functions. Creating copies allows you to run tests, which is important to ensure that all functions work correctly without interfering with the main working version.
- Compliance with legislation. Creating backups makes it possible to comply with legal requirements for the protection and safety of data if they are contained in a database or on a website.
Copying types
There are several most common types of backups:
- A full backup is the most complete and reliable type of backup (usually takes up a lot of disk space). This is a complete copy of all information located in the database or on the site.
- An incremental backup is a copy of only the data that has been changed since the last full or incremental backup. This option allows you to save time on creating backups, as well as reduce the amount of stored data.
- A differential backup (takes more disk space than an incremental backup, but less than a full backup). This type creates a copy of all changed data since the last full backup.
Next, we are going to consider two main ways to create file backups:
Self-service backup. Using this approach means that the user selects the files that need to be copied himself. User copies them to external drive or cloud storage. this process requires concentration and responsibility, since incorrect selection of files or errors in saving data can lead to loss of information.
Automatic backup. This approach is easier. It is more reliable as well. Using necessary tools embedded into the operating system or special software allows to automate the process of creating copies. Two most important advantages of this method are:
- saving time (this process runs automatically in the background),
- more reliable and regular backups creating.
One way or another, all types of backup have their advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a specific type, you need to pay attention to the technical architecture of the site or database, available resources and features of user requirements.
Setting up backups creating
Let's consider several tools for creating data backups (for using them on computers, servers and in the cloud):
- Network storage. SAN (Storage Area Network) or NAS (Network-Attached Storage) allow you to automatically create and store backups on network drives;
- Third-party data backup programs (including such types of data as: Paragon Backup & Recovery, EaseUS Todo Backup, Acronis True Image, etc.);
- Backup to external drives (the most accessible, convenient and easy way to store important information). You can use SD cards, USB flash drives, external hard drives and many others to create backups;
- Embedded OS tools. For example: Windows Backup and Restore or rsync for Linux, Time Machine for macOS. The Serverspace knowledge base contains instructions for creating backups using Windows Server Backup and using rsync on Linux;
- Plugins. You can install plugins to backup your WordPress site. Plugin examples: UpdraftPlus WordPress Backup Plugin, BackWPup, All-in-One WP Migration;
- Creating automatic backups on servers in the cloud is possible using cloud services (iCloud, Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive) and cloud providers.
There are also several useful steps for creating cloud backups for photos and other content:
- Select a backup service (based on your needs). We recommend paying attention to the editing capabilities, ease of use and sharing of content;
- Select the server or data you want to back up (it can be various documents, videos, photos and other files);
- Set up the frequency of backups. To do this, you need to set the frequency of creating backups, which will allow you to regularly save data;
- Check your backups to make sure they are not damaged and saved correctly.
Reducing the risk of information loss is possible through regular backups.
It should be remembered that ensuring maximum safety of information is possible through the use of several sources of data backup.
Setting up backup on the server
Next, we'll consider how to set up a backup server using 3HCloud as an example. There are two connection options on the data backup server:
- Connecting backup to a third-party server through an additional tool (required data is saved to S3 Object Storage).
- Connecting backup for a server created in 3HCloud.
Creating a new server requires connecting a backup using the «Scheduled backup» field, as well as selecting the storage depth of copies.
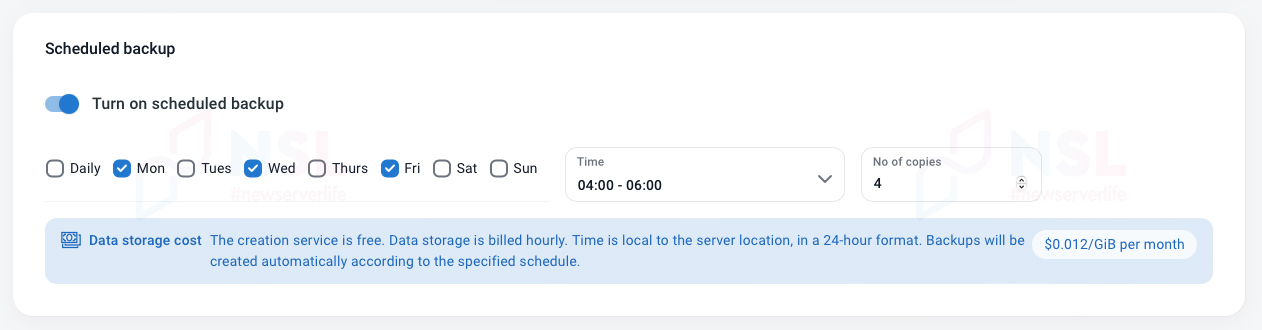
In the system disk settings (System Volume) in the “Automatic backup” section you can connect the service for an already created server (do not forget to indicate the storage depth of copies).
Backup is performed on a geographically remote disk array. This makes it possible to effectively and quickly restore data in case of loss. Old copies are automatically deleted after new ones are created.
3HCloud also provides another option – snapshot.
Snapshot represents instant recording of the application or system status for a limited time. Snapshots are usually used to create a copy of a virtual machine in its current state, as well as to safely and quickly restore the system to a certain level.
Snapshots in computer systems: in this case they are commonly used in virtualization to save the current state of the virtual machine (including files, apps, operating system).
Most often, snapshots are created before testing updates on the server. In case of problems, this will allow you to quickly “roll back” the system. We also do not recommend using snapshot as your primary backup tool.
To save backups to object storage on an existing server, you need to connect a third-party service (Veeam Backup as an example).
How to restore a server from a backup
Restoring a site from a backup depends on the chosen method of creating a backup. Another important point is where the copy is stored.
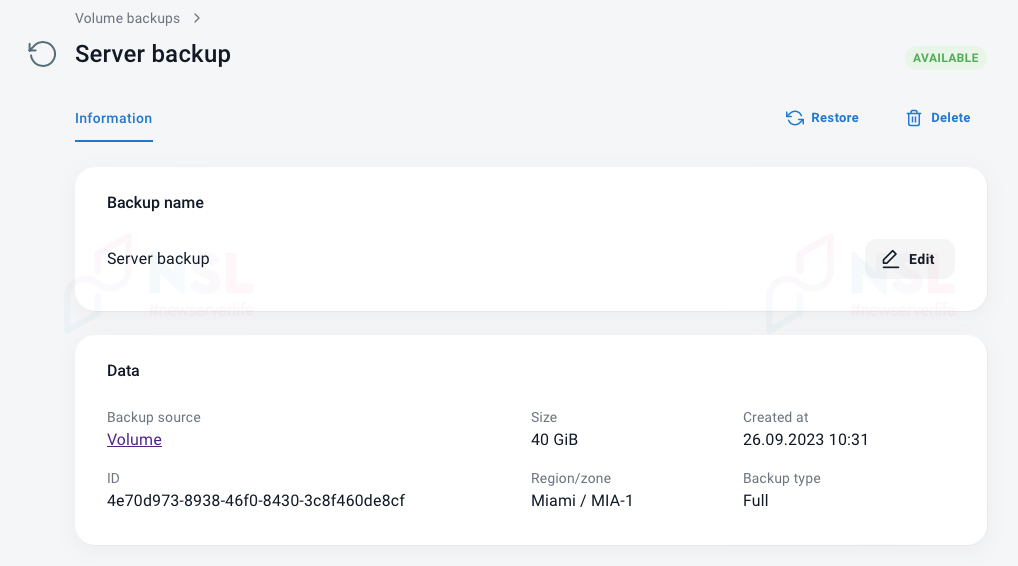
If the virtual server backup was connected to 3HCloud, then you need to:
- Go to the “Volume backups” section in the control panel;
- Select the required backup;
- Find the “Restore” button on the backup page.
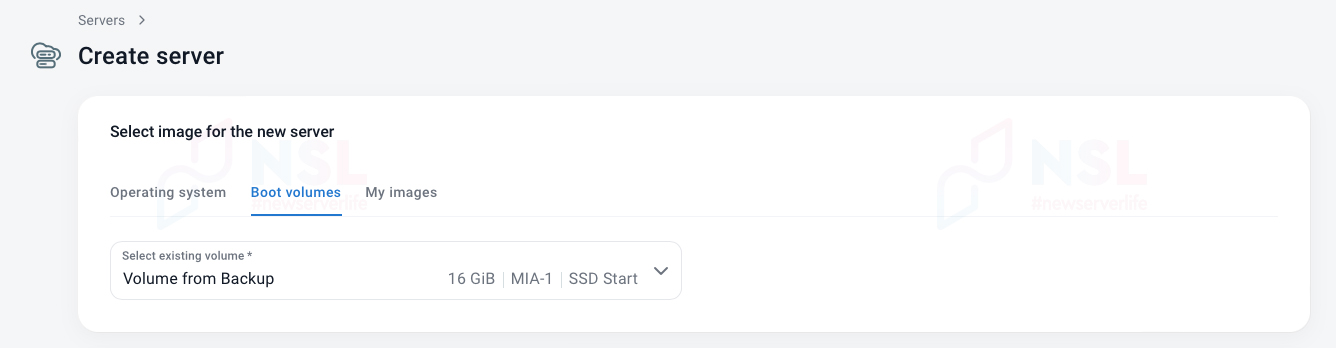
A new disk will be created from the backup. By selecting “Boot volumes” in the “Select image for the new server” section, you can create a new server from this disk.
In the case when the backup copy is stored in object storage, to restore the site it is necessary to use specialized backup tools, which are capable of performing the function of restoring from storage (for example: Veeam Backup & Replication).
Conclusion
Thus, backup is an important means of protecting and preventing data from loss in case of user errors, virus attack, hard drive failure, etc. It is also worth remembering to regularly create backups of the necessary data and use secure storage facilities to store them.
Specialists of our company are ready to help you purchase the server and select the necessary server configuration for any required task.













































