One of the key parameters when choosing server hardware is its form factor. Form factor refers to standardized case dimensions that ensure the most optimal placement of equipment in special racks and cabinets. The form factor also determines the maximum possible number of elements installed in the equipment.
In this article, you will learn about standard server form factors, mounting blocks used to measure their height, as well as important features of tower, rack and blade systems. The information presented in this article will be helpful in selecting the right equipment based on your organization's requirements, and budget.
Standardized server height units
In order to standardize the height of server cases and simplify the process of placing them in specialized racks, units (U) (1 U = 1.75 inches or 44.4 mm) are used for measurement.
The 19-inch standard for server racks means that the height of the equipment installed on each shelf is a multiple of 1U. This allows you to calculate the rack capacity in advance and use this space as productively as possible to accommodate servers of the desired size.
The organization's choice of server form factor should be based on the number of components that is possible to install in it. The greater the height, the wider the internal space of the case and the more powerful the configuration. Next we will consider the most popular options.
1U: small and inexpensive servers for offices
The first option is 1U servers – the smallest standardized models. They are usually called thin or narrow servers because of their small height (only 1.75 inches or 44.4 mm).
Pros of 1U servers:
- Low cost. These server models are often much cheaper compared to higher servers, given that most of the characteristics are equal.
- Compactness. Occupies minimal space when mounted in racks.
Due to the small size of 1U servers, they have certain limitations:
- Typically, only 1 CPU can be installed in a 1U case;
- There is a limit to the number of slots for expansion cards;
- The number of drives is also limited: on the front panel there is a maximum of 8-12 drives (2.5-inch format) or 4 drives (3.5-inch format);
- Due to the high density of components, node cooling and thermal package limitations are sometimes an issue.
The 1U server models from Supermicro are a suitable option for small offices where simple tasks such as deploying web servers, mail services and file storage are performed.
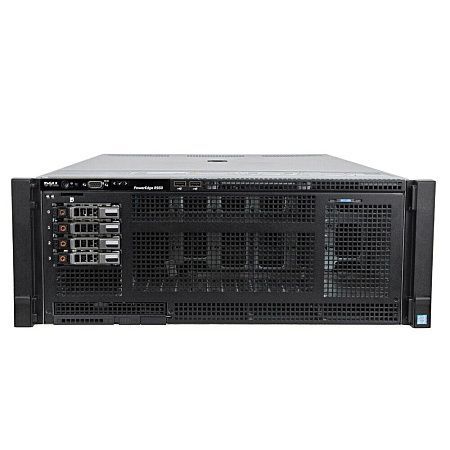
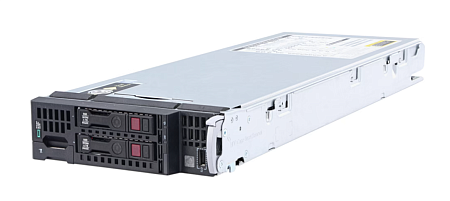
Below is an example of a 1U server
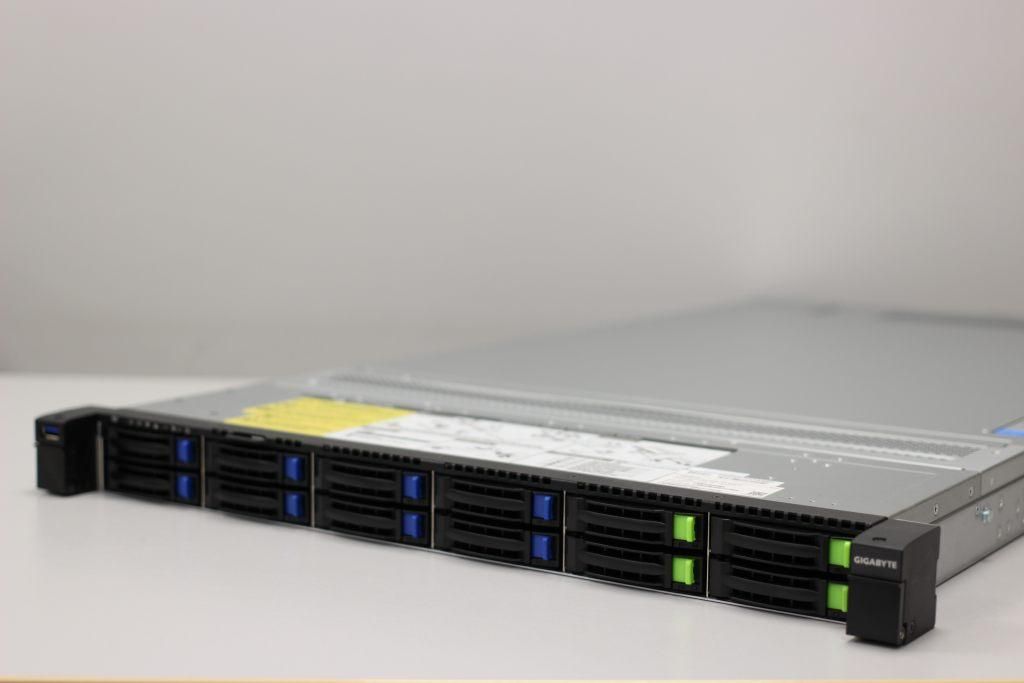

2U: a universal option for medium-sized businesses
Servers with a height of 2U are twice as high as a 1U server. More powerful configurations can be installed in such server models:
- Up to 4 CPUs;
- Up to 16 expansion cards or 8 dual-slot accelerators;
- Increased number of drives: 10-25 drives (2.5-inch format) on the front panel.
The main advantages of 2U servers over compact 1U models are:
- The ability to install the server horizontally and vertically in a rack;
- Improved cooling achieved by free space for fans and heat pipes;
- Providing a higher level of performance for complex operations and tasks.
For example, Supermicro 2U servers have become widespread among medium-sized businesses due to the most optimal balance of such indicators as compactness, performance and price. These server models can be used to perform numerous tasks of various categories.
Below is an example of a 2U server
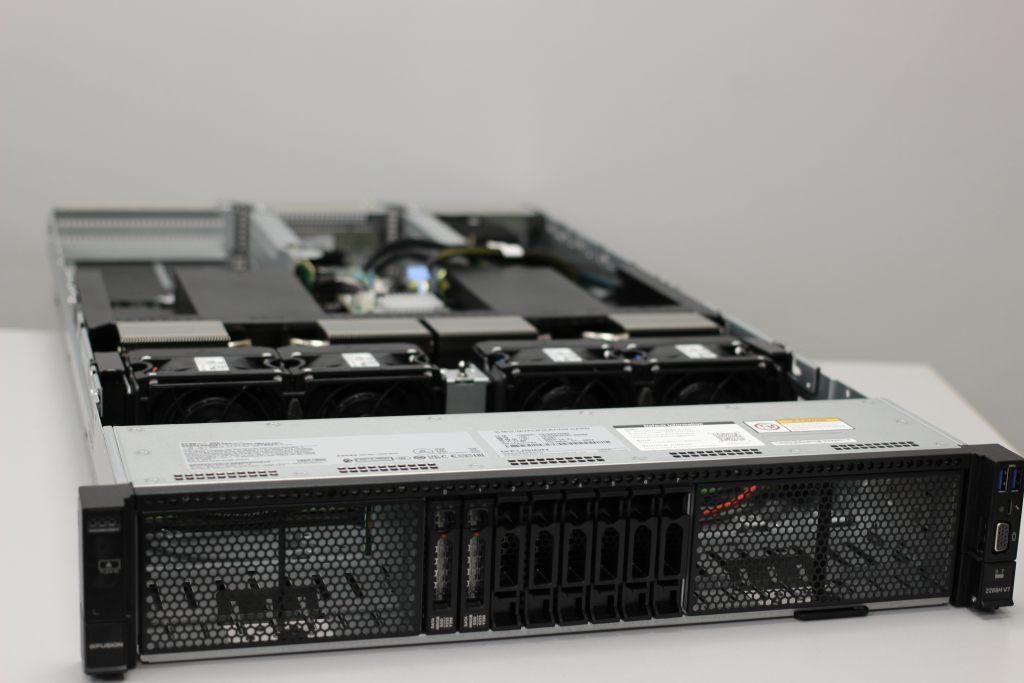

3U and 4U: powerful servers with increased capacity
3U and 4U servers are characterized by even greater case capacity. This feature makes possible to install the following components in them:
- Up to 4 CPUs with 6 dual-slot accelerators for high-performance computing;
- Up to 99 drives with a capacity of up to 22TB each.
Due to this hardware power, 3U and 4U servers are an excellent choice for working with applications and tasks that require a high level of efficiency and a large amount of memory with fast access:
- SAN and NAS storage systems;
- Virtualization of servers and desktop operating systems;
- Image processing, video editing, 3D rendering.
Due to the optimal combination of performance and cost, AIC 4U servers have become especially popular among large corporations. Among the disadvantages of such server models, it is worth noting the complexity of cooling and a significantly high price. For this reason, they are typically used in data centers.
Below is an example of a 4U server
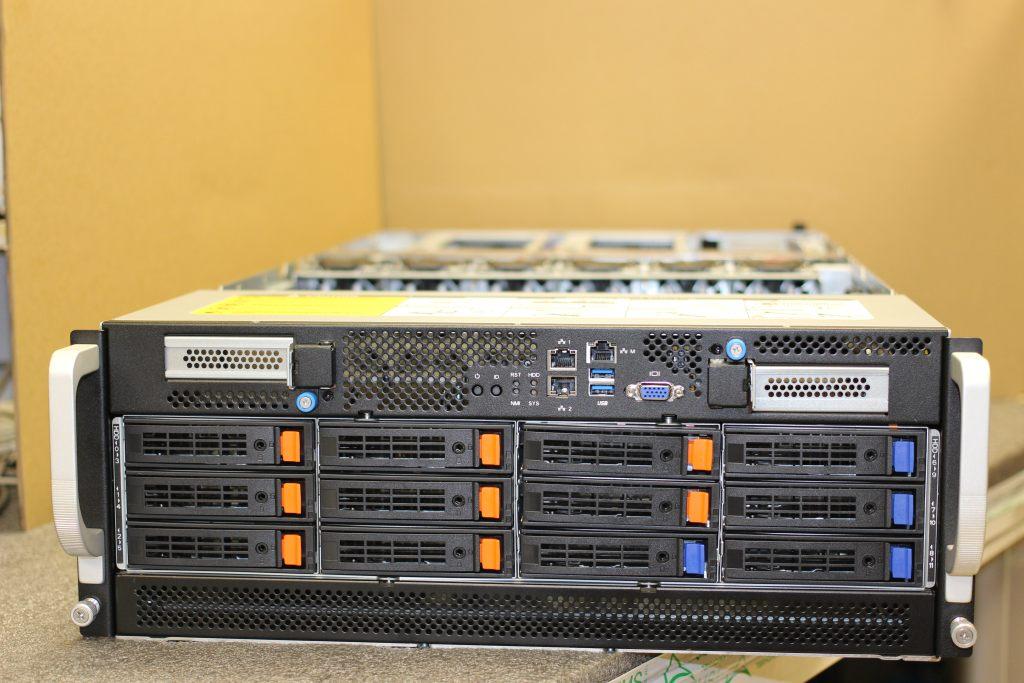

Tower servers: flexibility for off-rack installation
In addition to the standard rack-mounted form factor, there are Tower servers. They are similar to PC system units (they also have a vertical shape). Tower servers are provided in full, medium, and low height.
Flexibility in installation is the most important advantage of Tower servers:
- If the case is mounted on rails, it can be installed on tables, shelves, or in server racks;
- If the case is of suitable design, it can be installed vertically or horizontally.
The design of these servers ensures the convenience of their use in situations where it is not possible to purchase server racks. For example, Tower servers from Supermicro are a good solution for small offices.
Among the disadvantages of Tower servers are usually:
- non-standard shape,
- large dimensions.
If you do need to install them in a rack, you will have to purchase special mounting or conversion kits for tower servers.
Below is an example of a Tower server
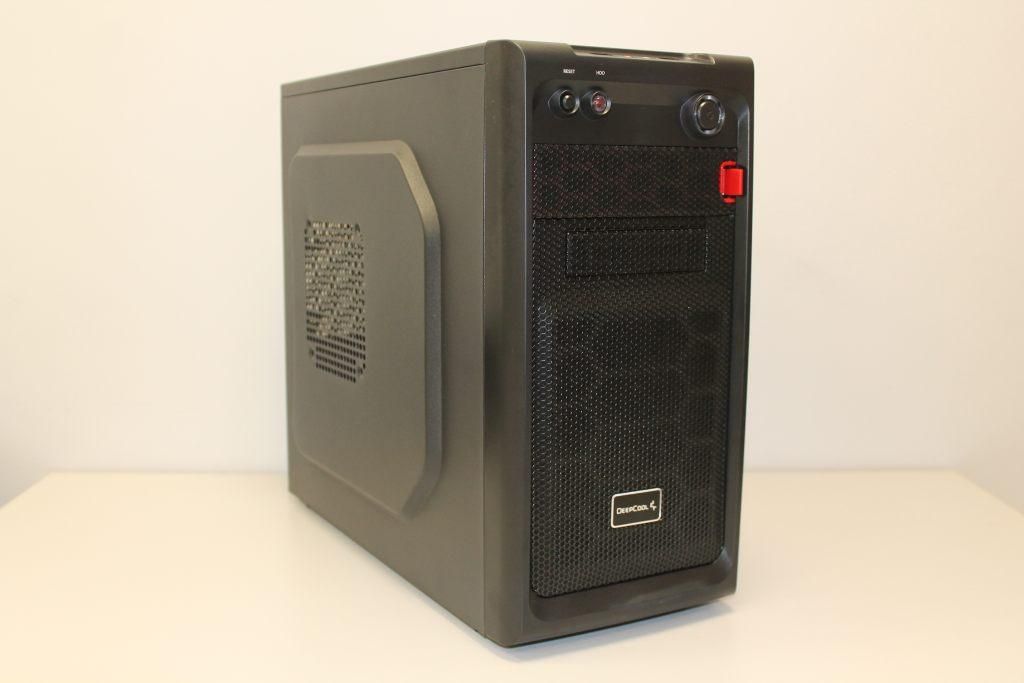

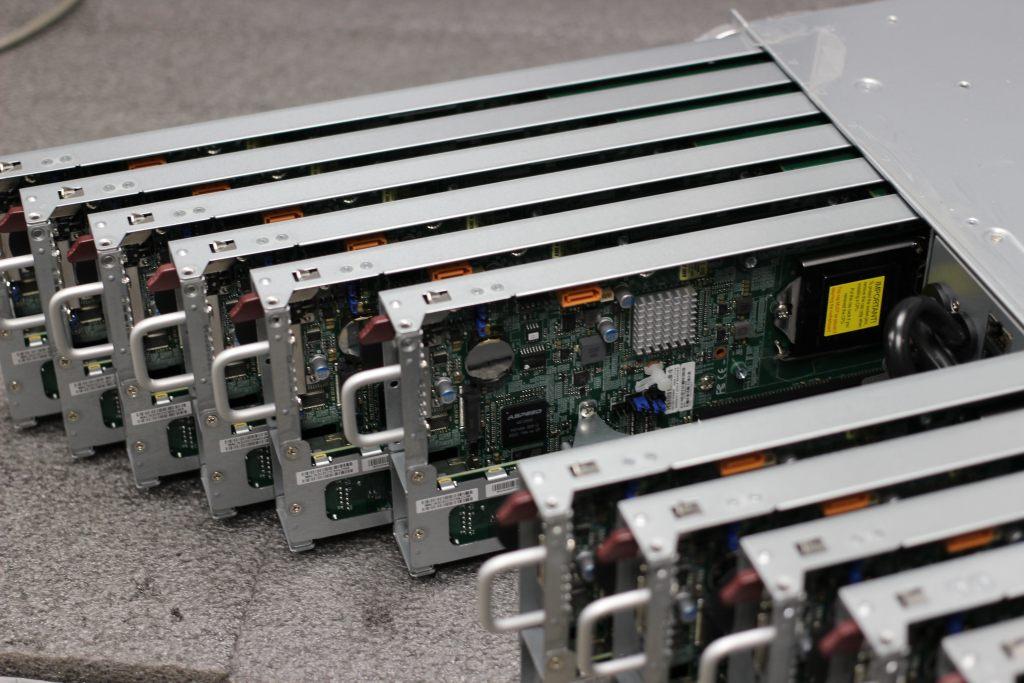
Blade systems: development for compact and powerful solutions
Blade server is a modular component designed in order to create high-performance computing systems. Individual blade servers look like thin circuit boards. They are installed in special cases called blade chassis.
Blade systems do not have their own power supplies, fans, or connectors. These components are embedded into the chassis. Blade system boards place only the most important elements:
- Processors (1, 2 or 4 CPUs);
- CPU cooling system;
- RAM (from 32GB to 2TB);
- Connectors for connecting to the common chassis bus.
Next, we will consider the main advantages of Blade systems:
- Customization flexibility. Blade servers with different numbers of processors and RAM can be combined in one chassis to solve numerous tasks of various complexity.
- High-density placement. The number of server boards that can be installed in a chassis starts from 10 boards and more. This makes it possible to simplify scaling processes and save space in the data center.
- Easy maintenance. To upgrade or replace an outdated or failed server, all you need to do is remove one blade module from the chassis and insert another.
Among the disadvantages of Blade systems, it is worth noting the complexity of the initial selection of the chassis based on certain characteristics and the high cost. That is why Blade systems are mainly used in large data centers.
Below is an example of a Blade server
Criteria for selecting the server form factor
Below we will consider the main criteria that you need to pay attention to when choosing the optimal server form factor:
- Installation type: server rack or table. It is worth remembering that rack servers are more difficult to maintain on your own;
- The required amount of disk capacity. Here we are talking about the number and type of drives (HDD, SSD) that have to be installed in the case.
- Required speed and type of network connections (1 Gbit, 10 Gbit, 40 Gbit, Infiniband).
- Possibility of further scaling. With ProServer, you'll be able to upgrade the system as your workload increases.
- Additional expansion cards (network adapters, video cards for workstations).
- The requirements for server performance depend on the number and categories of tasks that are planned to be performed.
- Project budget. Form factor and configuration determine the final cost of servers.
Companies should choose a server form factor taking into account all the important points discussed in this article. The information provided will help you select the most suitable server to meet your current and future business needs. Along with the height of the case, it is necessary to take into account the type of construction: rack, tower or blade.
Thus, the right choice of server form factor will ensure the most efficient allocation of the budget for IT infrastructure, and will also eliminate unnecessary expenses on modernization.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right server form factor is crucial for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of your IT infrastructure. By understanding the various options available, from standard rack-mounted servers to tower servers and blade systems, you can tailor your hardware to meet your organization's specific needs. Consider factors such as installation type, disk capacity, network connections, scalability, and budget to make an informed decision. With the guidance of Newserverlife, you can confidently select the ideal server form factor to support your current operations and future growth. Invest wisely in your IT infrastructure to ensure seamless performance and scalability for years to come.
Specialists of our company are ready to help you purchase the server and select the necessary server configuration for any required task.