In recent years, the Internet users increasingly faced with a problem of "heavy" content, causing a decrease in the loading speed of websites and services. It doesn’t have the best effect on the activities of companies with a widely distributed audience across the regions or the countries and the developers of mobile applications and the multimedia projects. Content delivery networks (CDNs) help solve current problem.
What is CDN and its benefits
CDN (Content Delivery Network) is an IT infrastructure in the form of a network where the users of web services and the websites receive a content at higher speed. At the same time, the servers belonging to this network distributed geographically in such a way as to minimize the response time from the service or site.
A number of terms also related to the concept of CDN:
- origin - a server for the storing source data or the files transmitted via CDN;
- PoP (point of presence) – the caching servers included in CDN and related to the specific geographic locations. These servers also referred as an edge term;
- dynamic content - generated content on a server when the request is received. This content could be modified by a user or loaded from a database;
- static content – the binary files, audio and video materials, JS and CSS stored on the server unchanged.
The use of Content Delivery Network provides a number of advantages:
- improving SEO due to faster site loading and increasing its priority in the search results;
- reducing the cost of creating infrastructure. That is a purchase and an implementation of additional equipment and increasing a performance of the origin server - the main operation work on CDN;
- higher site availability - in the event of a system failure traffic redirects from a faulty CDN server to a reserved one;
- formation of the detailed and up-to-date traffic statistics data in real time;
- the possibility of a global coverage - the availability a site with anywhere;
- offloading a source server by transferring a content through CDN servers.
Also, advantages of this network include the simplicity of the CDN and the relatively low cost of services with CDN providers.
Principle of a process
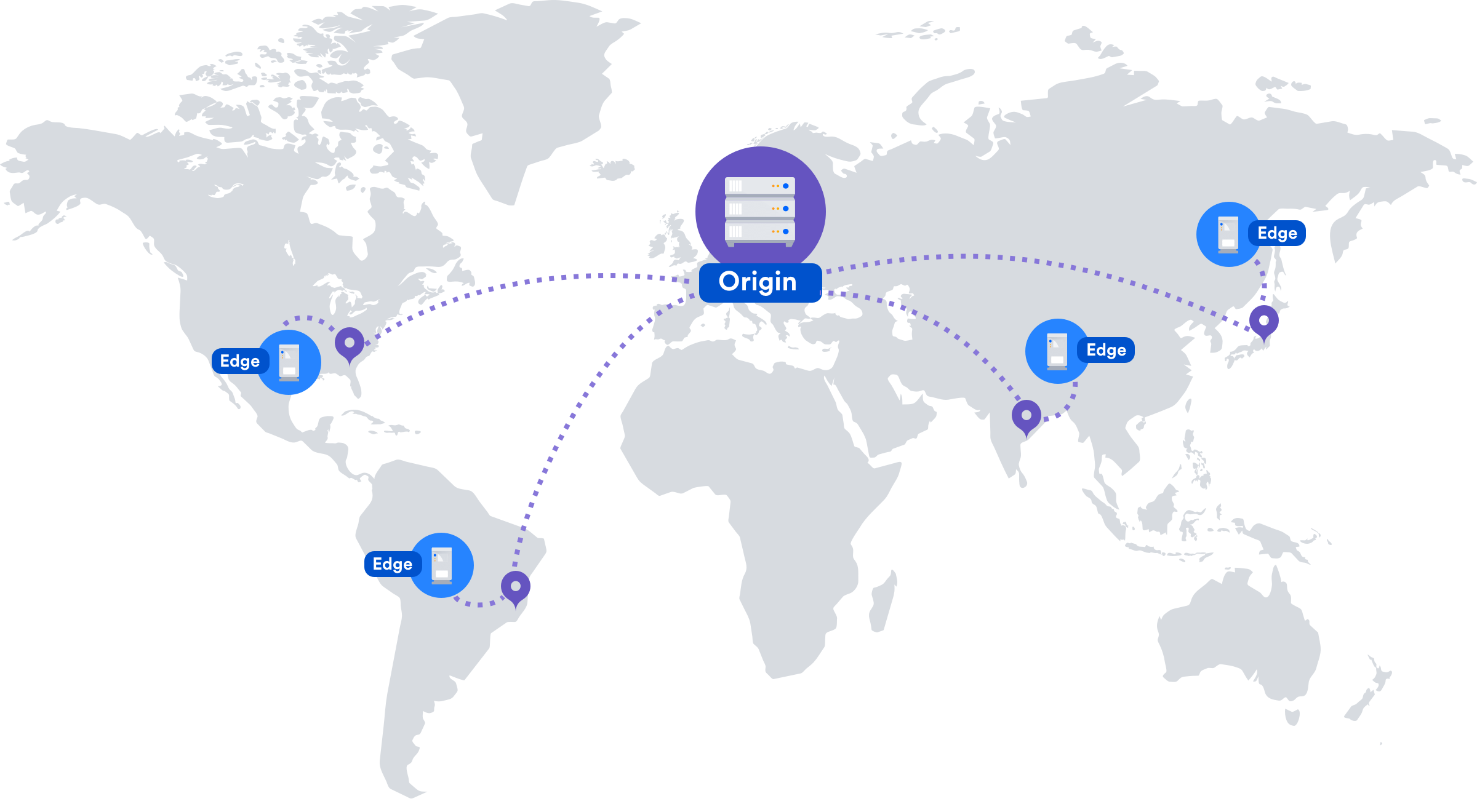
In contrast to transfer a data on the regular hosting according to scheme “a client requesting certain content from a data storage server - processing a request by server and transferring a data packet to them - downloading a site”, CDN uses the principles of the caching and shielding in its work.
Caching is the loading of a content from the origin server to CDN server with its subsequent distribution to the site visitors depending on their geographic location. This principle helps significantly increase the speed of a site loading.
However, since the caching could occur with delays in a displaying content due to increased load on a source server, the shielding solve this problem. Installing an intermediate server between the main and CDN server. This intermediate server caches a content and then distributes it to CDN servers.
Using the shielding solves several problems at once: a source server protects with the overloads, a fault tolerance of CDN increases and a cache updates without delay.
Content is loaded from CDN using two popular technologies - GeoDNS and AnyCast. GeoDNS allows to associate one domain name with multiple IP addresses and redirect a user to closest server in terms of geographic location (which is determined by IP address).
AnyCast technology uses the shared addresses with routing to servers within a specific region. Redirection to nearest point of presence carries out when a user contacts www.example.com. Different networks with a point of presence send an announcement to user's provider and the closest one selects by router and the answer also sends by shortest route.
How to set up CDN
For setting up the distribution of static content via CDN a web resource administrator needs to do:
- create the origin by placing site statics on a separate domain (for example, on static.example.ru or static.example.com);
- work via CDN, create a domain cdn.example.ru or cdn.example.com;
- connect a CDN with a provider, informing him of the domains addresses for placing statics and distributing content;
- set up a CNAME record from cdn.example.ru (com) at your DNS registrar to domain allocated by CDN provider upon connection (that generates automatically;
- change a domain name on your site to cdn.example.ru (com) - for statics distributed via CDN.
Static content, as a rule, places in the object storages integrated with the cloud services, and its distribution via CDN is carried out using plugins and extensions for CMS (1C Bitrix, Drupal, Wordpress, Joomla and others). The work of web service after connecting the CDN continues on original server and the parts of site intended for caching host on CDN servers. At the same time, such content updates periodically.
Disadvantages and the alternatives
Despite the convenience of CDN technology, it has some disadvantages:
- a risk of caching delays associated with changes to the original file on central server during the keeping old version on caching servers. For solving this problem it is necessary to clean and update the cache pools from time to time as well as manage settings using validator headers;
- the possibility of site’s blocking caused by blocking of the “neighboring” services by IP from CDN provider. In such cases you should contact the provider and change the IP address.
An alternative option for a content distribution network can be cloud VPS / VDS hosting with the great scalability, high security and with a fault tolerance. However, the cloud hosting maintenance requires a work with the professional programmers. So the cost of this solution will be higher.
What to look for during the choosing CDN provider
During the choosing CDN provider you should pay attention to:
- the number of presence points and a coverage area. For projects with a large coverage of an international audience it is important to have the points of presence in the regions that are “richest” with the potential users;
- the quality of interaction between CDN provider and the telecom operators affecting directly the speed and efficiency of a content distribution through the network;
- the presence of convenient service control panel with an extensive arsenal of tools for analyzing consumption statistics, managing caching policies, managing HTTP headers, preloading very "heavy" (from 200 MB or more) content, full and selective clearing of the cache;
- high level of security - site and caching CDN servers should be protected by cryptographic SSL certificate and they should work using HTTP / 2 and IPv6 protocols.
The specifics of the company's business plan also influence a selection of CDN provider. Therefore, if you need to find the best solution in this area, please contact the specialists of our company.
Specialists of our company are ready to help you purchase the server and select the necessary server configuration for any required task.