An active transition of the operation services and data warehouses into online environment reformed with an integral part of modern business and startups. At the same time, the operation of online products, the using of data centers and a business in general are the subject to DDoS attacks making the systems inaccessible to users, resource owners and to managers.
IN Q4 2021, KASPERSKY LAB REACHED A RECORD OF NUMBER’S GROWTH DDOS ATTACKS - BY 52% AND BY 4.5 TIMES, COMPARED WITH THE PREVIOUS QUARTER, AND BY 4.5 TIMES COMPARED WITH THE LAST YEAR. THE NEWS, BUSINESS AND THE FINANCIAL SERVICES PARTICULARLY SUFFERED. SUCH A MARKET SURGE WITH DDOS IS DUE TO THE CHANGES OF GLOBAL ECONOMY CAUSED BY CORONAVIRUS PANDEMIC.
What is a “server attack” and a DDoS attack. Who needs it?
A term DDoS created from the abbreviation DoS - “denial of service”. The word added - “distributed”.
DoS-attack is an artificially generated significant increase in a load on the servers or sites by increasing the flow of requests from a device. Such attack leads to partial or complete "paralysis" of global infrastructures or individual Internet services, caused by a decrease in the limited resources of service - the number of simultaneous user sessions, the width of connection channels, and server RAM.
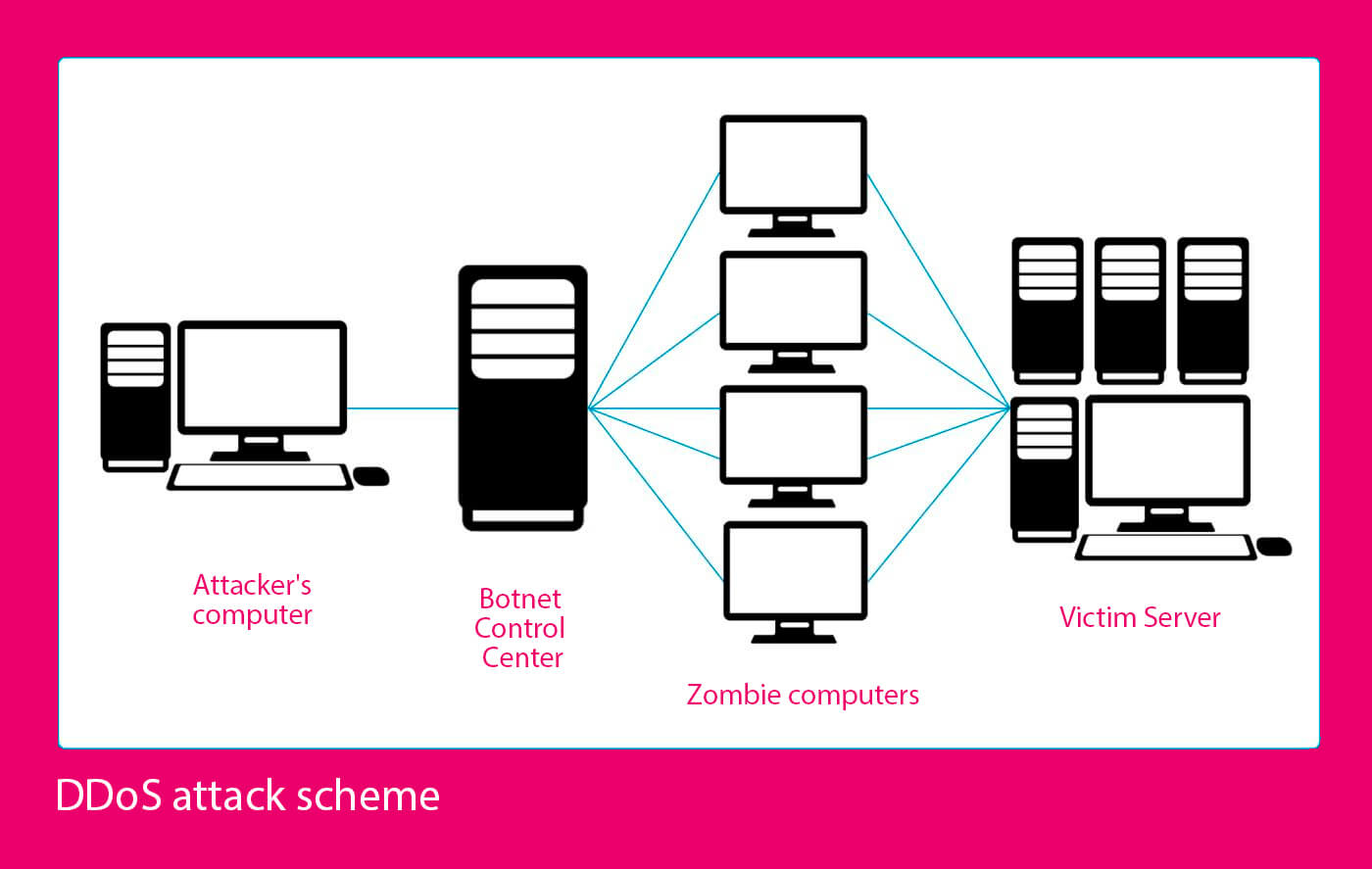
DDoS attack scheme
In case of DDoS attack, there are several devices that attack a server (botnets). These attacks are most often carried out to fight the competitors (reduce traffic to their sites, reduce sales or completely unavailability of resources for users), to conduct the fraudulent activities and to steal a personal data.
According to research by Qrator Labs, in 2021 by cybercriminals were attacked the companies to collect an information with retail the chains and e-commerce organizations becoming the most frequent victims.
Classification of DDoS attacks
In OSI model used in the Internet, there are 7 levels of communication media: from the first level (physical environment) to seventh level (applications). At the same time, all these levels are subject to DDoS attacks. Each of them described in more detail in the table.
| OSI layer | Data type | Level’s description, the protocols | The nature of DDoS attack | Result | Way to solve a proble |
| 7th (Applied) | data | Start creating the data packages. Joining and accessing a data. The custom protocols FTP, SMTP, Telnet, RAS | PDF GET requests, HTTP GET, HTTP POST (website forms: login, photo/video upload, feedback confirmation) | Exhaustion of resources on attacked server due to their excessive consumption | Systematic monitoring of application software to identify 0day application of the vulnerabilities. At level 7, it is easiest to detect and eliminate the attacks |
| 6th (Representative) | data | Broadcasting a data from a source to recipient. Data compression and encoding the protocols (ASCII, EBCDIC) | Spoofed SSL Requests: checking SSL encrypted packets is a resource intensive, the attackers use SSL for HTTP attacks on victim's server | The attacked systems stop accepting SSL connections or rebooting automatically | The need to use a distributed SSL encryption infrastructure (hosting SSL on a standalone server if it’s possible) and inspect an application traffic for attacks or the policy violations on application platform |
| 5th (Session) | data | Management of the establishment and termination a connection, synchronization the communication of sessions within an operating system via the network (in period of logging in/out). Login/Logout Protocols (RPC, PAP) | Attack on Telnet protocol exploits the weaknesses in Telnet server software on switch, making a server inaccessible | Admin can't manage a switch | Support a firmware up to minimize the attack risks |
| 4th (Transport) | segments | Ensuring a transmission of an information between the nodes without errors, managing a transmission of messages from 1 to 3 levels. Protocols TCP, UDP | SYN flood, Smurf attack (attack with ICMP requests by changed addresses) | Exceeding the threshold values for channel width or the number of allowed connections failures in operation of network | Using DDoS traffic filtering system by blackholing technology |
| 3rd (Network) | packages | Routing and transfer the information between different networks. IP, ICMP, ARP, RIP protocols and the routers that use them | ICMP flood - DDos attacks that overload the target networks with ICMP messages and reducing their throughput | Firewall overload | Limitation the number of requests processed via ICMP protocol and the reducing an impact of current traffic with a firewall speed |
| 2nd (channel) | frames | Installation and maintenance of message passing at physical layer. 802.3, 802.5 protocols, as well as the controllers, access the points and bridges that use them | MAC flood - oversaturation of network switches with the data packets | Blocking all ports with the data streams | Setting the switch settings for filtering |
| 1st (physical) | bits | Transfer of the binary data. 100BaseT, 1000 Base-X protocols, as well as the hubs, sockets and patch panels that use them | Creating the physical obstructions and disruptions in network assets | Falling into disrepair of network equipment up to the repair and replacement | Systematic monitoring the technical part of network equipment |
In addition, the following types of DDoS attacks are distinguished:
- HTTP and POST flood - traffic imitates HTTP and POST requests. “Empty” data loads to a server or sends from a server. The transmission channels overflowed and the server resources spent with the current requests;
- Ping of Death is a type of protocol attack using the packets designed to crash a system on server side. It’s a sending of data packet larger than 65,535 bytes. The attacks extending on ICMP and other protocols. As a result, a server hangs and crashes;
- DNS flood - UDP flood version for a specific application. A huge number of fake DNS queries sending on DNS server to overload it. DNS server crashes due to the overloads and the website then is unavailable;
- DNS amplification attacks - sending empty, typical requests (the data packets) to a server. The attacker sends DNS lookup the requests, replacing a source IP address with a victim IP;
- Amplification attack, when a small number of the bots initiate sending a significant number of the fake packets or requests;
- Fraggle Attack uses the large amounts of UDP traffic on router's broadcast network. Current attack works similarly to Smurf attack but uses UDP broadcast protocol instead of ICMP;
- Pulse Wave with periodic bursts of traffic. A typical DDoS attack looks like a gradually increasing stream of a malicious traffic. Pulse wave is a series of short periodic pulses occurring at a high power;
- APDoS aimed to create a most serious damage to attacked server. APDoS uses the mechanisms of HTTP flood, SYN flood and other types of the attacks. It sends the millions of requests per second;
- Slowloris attacks target web servers. The attacking servers connect to target servers and keep connection half-open for as long as possible and then propagate those half-open connections. Such connections closed by attacked server if timeout slower than new ones established. Counteracting this attack is quite difficult, since the sources of attacks are practically untraceable;
- NTP amplification attack uses Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers that are responsible for the synchronizing computer clocks on the network. A goal of attack is to overload with UDP traffic. In these cases, the attacked server responds by sending UDP traffic to IP address spoofed by attacker. "Gain" means that the amount of UDP response traffic is much larger than the request. Therefore, the network quickly overloaded with a parasitic traffic and its nodes stop working.
How to stop a DDoS attack
If a DDoS attack occurred, you should:
- quickly identify a fact of attack and its source. It will help stop the attack and reduce a possible damage. You could determine where the attack comes from through a profile of incoming traffic with the indicators of volume and channels of receipt. Deviations from current profile often signal the start of DDoS attack;
- Allocate server bandwidth headroom up to 500% once. Such a margin will give time to recognize a source and a type of the attack and take measures to protect against DDoS before a server completely "crashes";
- protect the network perimeter by limiting a speed of router, install a filter system to the drop packets from recognized attack sources, set a timeout for half-open connections (where no confirmation from the request source was received during timeout), lower the drop thresholds for SYN-, ICMP-, and UDP -flood.
Although current measures cannot completely protect against DDoS attacks, they could buy time to resolve a problem before it irreversible.
The tips concerning preventing DDoS attack
For avoiding a denial of service, there are several ways to prevent DDoS attack, such as:
- set “checkpoints” in order to “mitigate” the consequences and roll back a system in the event of attack;
- infrastructure preparation - creation a monitoring system to detect the first signs of attack, a system for redirecting and eliminating DDoS traffic, installation the stable network components that are adaptive to the attack scenarios with increased traffic load;
- creation a working group and current plan to eliminate DDoS attacks;
- use CDN for balanced distribution of traffic between the servers;
- use a cloud and the hybrid servers to increase a bandwidth and improve a cybersecurity;
- use the services of web hosting companies and DDoS attack specialists;
- use a hardware, software and the specialized anti-DDoS tools - network firewalls, firewalls for web applications, protection for border session controllers;
- ensuring the protection of DNS servers by their reservation and distribution in the various data centers.
Such measures will help ensure a server's performance even with DDoS attack.
DDoS attack for the benefit - how to organize the attack on a server to check a fault tolerance
For finding out with what extent an information system (IS) is able to withstand to overloads and maintains a resistance to the redundant requests, it is recommended to conduct a stress test with an imitation of DDoS attack in a controlled experiment.
Stress test of a system for a fault tolerance is most often carried out:
- before launching a business and the web applications, DBMS and remote the banking services;
- during the regular work with critical applications used constantly;
- after making changes to settings or configurations of the information systems.
Imitation of DDoS attack allows find out the normal ranges of loads, determine the level of effectiveness of existing protection systems, evaluate the quality of providers’ actions and information security services in detecting and blocking DDoS attacks, identify the most vulnerable points of information system and take measures to increase its resistance to the attacks.
Simulated DDoS attacks carry out on pre-selected test the objects with established results criteria, according to a pre-compiled schedule. For the test objects, the scenarios are developing and the selected tools are monitoring, the resources are calculating for a generating network traffic. A stress test conducts in a production or in a test environment.
The following utilities could be used for monitoring during IS testing:
- LOIC or Low Orbit Ion Cannon is an open source program that is great for testing DDoS attacks. The main goal of a program is to test the network through a large number of TCP, UDP and HTTPS requests;
- DDOSIM layer 7 simulates a DDoS attack with the multiple random IP addresses. Its way you could assess realistically the ability of your server to withstand the attacks such as "denial of service";
- RadView is suitable for the performance checks of mobile, cloud, a server and for the web applications;
- Apache JMeter - when assessing IS stability at different load levels.
The efficiency and a fault tolerance of an IS are evaluated by basic indicators - response time, the ratio of completed and unsuccessful transactions per unit of testing time, processor load at peak values, throughput under attack, the amount of a storage required by application to process the multiple requests.
A few words about another network attacks
In addition to DDoS attacks, there are other network attacks:
- Mailbombing - attack on the mailbox, leading to its overflow and even to the failure of mail server;
- buffer overflows - search for a software or the system vulnerabilities that could lead to crashes of applications or to execution of arbitrary binary codes on behalf of a user (up to full control over the computer);
- Rootkit, package sniffers and the specialized programs infecting all computers in IS, work to intercept the names and passwords to hide the files, system services, folders and the drivers from a user;
- SQL injection means attack that changes the parameters of SQL queries to a database. As a result, the request’s meaning is distorted and in case of incomplete filtering of data input, not only confidential information could be lost but the data could also be changed or deleted;
- XSS - attack to steal Cookies storing the information about the personal data of site user and the encrypted passwords for entering sites;
- Phishing - theft through the spam or bots of confidential information or identification data of the organizations’ clients for further criminal purposes.
DDoS attacks are powerful tool in the hands of attackers that could cause a significant damage to a server and to the website owners. It is important to be responsible for protecting your own resources, take measures to prevent attacks. In the event of attack promptly identify a problem and solve it.




